Imagine a world where AI systems decide who gets hired, what medical treatment is recommended, or which social benefits are allocated. These decisions, although often perceived as impartial, can inadvertently perpetuate bias and discrimination, a phenomenon we have seen repeatedly in AI technologies. This is where AEQUITAS steps in.
Introducing AEQUITAS
AEQUITAS is a Horizon Europe-funded initiative designed to operationalise fairness within AI systems by embedding social-technical, legal and ethical considerations directly at the AI lifecycle.
As AI technologies become more deeply integrated into decision-making processes across sectors such as recruitment, healthcare and for socially disadvantaged groups, addressing issues of bias and discrimination is becoming increasingly critical. AI systems can unintentionally reinforce societal inequalities, but AEQUITAS provides a controlled experimentation environment where AI models can be stress-tested against fairness requirements. This ensures compliance with the EU AI Act, the Charter of Fundamental Rights, and the Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI.
AEQUITAS acts as a tool that integrates fairness into the AI lifecycle, shifting fairness from an afterthought to a core principle of design. It provides a structured methodology and a set of tools for assessing and mitigating AI discrimination and bias, ensuring that AI development aligns with both legal and ethical standards. This controlled experimentation enables the validation of fairness claims before AI systems are deployed into real-world applications.
Our objective: transforming fairness from an afterthought to a core principle
The mission of AEQUITAS is to transform fairness from an afterthought into a core design principle in AI development. Traditionally, fairness in AI systems has been addressed reactively, often after issues arise during deployment. AEQUITAS takes a proactive stance by embedding fairness into every phase of the AI lifecycle. This shift requires the integration of socio-legal, ethical and technical considerations early in the development process. By embedding fairness at the design stage, AEQUITAS ensures that AI systems are tested for biases, inequalities and discriminatory impacts before they are rolled out into society.
Our goal is to ensure that AI systems are developed responsibly and that fairness becomes an intrinsic part of the AI development process, rather than something that is merely assessed at the end of the pipeline. Through this initiative, AEQUITAS helps developers, researchers, and organisations to anticipate and mitigate fairness issues from the outset, ensuring a more equitable outcome for all stakeholders.
Watch our project video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0DDGj00YYmE
Our methodology: a holistic approach to AI fairness
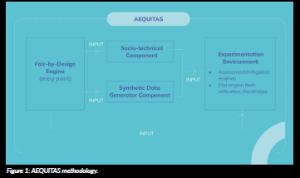
AEQUITAS’ methodology follows a comprehensive and holistic approach to ensuring fairness in AI systems. It is structured around several interconnected components that ensure fairness-by-design throughout the AI lifecycle. It is structured around several interconnected components that ensure fairness-by-design throughout the AI lifecycle and
that are seamlessly integrated to provide a unified framework. The methodology is designed to be adaptable to various sectors and contexts, ensuring that fairness is always contextualised according to the specific challenges and legal requirements of the application at hand.
AEQUITAS is structured around several interconnected components that ensure fairness-by-design:
1. Fair-by-Design (FbD) Engine
At the core of AEQUITAS lies the Fair-by-Design (FbD) Engine, which serves as the operational heart of the framework. To ensure that fairness considerations are addressed at each stage of the AI development cycle, the FbD Engine is responsible for organising fairness methodology into structured phases:
- Scoping: Defining the AI system’s purpose and identifying affected stakeholders.
- Risk assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential risks of bias and discrimination.
- Development and evaluation: Implementing fairness metrics and applying mitigation strategies during system development.
- Deployment and monitoring: Ensuring transparency, accountability and ongoing fairness evaluations post-deployment.
- Re-evaluation: Periodic reassessment of fairness metrics to ensure continued compliance with evolving legal and societal standards.
2. FairBridge
The FairBridge engine is a modular decision logic system that underpins the FbD Engine. It encodes fairness reasoning into a dynamic question-answer (Q/A) framework. The Q/A system acts as a guiding structure, helping users select fairness metrics, identify sensitive attributes and recommend mitigation strategies based on socio-legal requirements. FairBridge operates primarily as a backend engine, integrated into AEQUITAS’ Experimenter tool. This integration ensures that fairness considerations are embedded into the AI system’s pipeline from the design to the deployment stage.
FairBridge allows for the customisation of fairness assessments based on the specific application of the AI system, making it adaptable across various sectors. The engine also supports the generation of compliance documentation, making it easier for organisations to meet regulatory requirements and for policymakers to track AI systems’ adherence to fairness standards.
3. Experimenter Tool
The Experimenter Tool is a user-facing orchestration environment that simplifies the implementation of fairness-by-design in AI systems. It allows users to upload datasets, configure AI models and conduct fairness assessments throughout the system’s development lifecycle. The Experimenter Tool integrates directly with FairBridge, ensuring that fairness metrics are applied at critical decision points during AI model configuration. It also provides tools for generating compliance documentation, audit trails and mitigation workflows.
4. Synthetic Data Generator
The Synthetic Data Generator module is an essential tool within the AEQUITAS framework. It can produce both bias-free datasets and deliberately polarised datasets to simulate various fairness scenarios. By testing AI systems with different data distributions, AEQUITAS can expose vulnerabilities and discriminatory patterns that may emerge under specific conditions. This synthetic data capability enables controlled stress testing of AI models, allowing researchers and regulators to evaluate the fairness boundaries of AI systems before they are deployed in real-world applications.
5. Socio-Legal Integration
The Socio-Legal Integration component of AEQUITAS ensures that technical assessments are aligned with fundamental rights, legal frameworks and sector-specific regulations. This integration captures the regulatory, ethical, and societal context of AI applications, ensuring that fairness assessments are not only technically sound but also legally compliant. The socio-legal component helps translate legal requirements, such as those in the EU AI Act, into actionable technical guidelines, ensuring that AI systems meet both ethical and legal standards.
The AEQUITAS Fair-by-Design methodology
The AEQUITAS Fair-by-Design methodology is a comprehensive framework that ensures fairness is embedded throughout the AI lifecycle. This approach involves the following key phases:
1. Scoping
During the scoping phase, the purpose of the AI system is defined, and stakeholders affected by the system are identified. This phase includes a fairness risk assessment to anticipate where biases might occur. Legal and social experts work with developers to establish the context and define fairness in a way that aligns with legal and ethical principles. This phase sets the stage for ensuring fairness by identifying the key issues early in the development process.
2. Risk assessment
In the risk assessment phase, the system undergoes a thorough evaluation to identify potential biases in the data, algorithms and outcomes. Developers, legal experts and social scientists collaborate to assess where unfairness might arise. By identifying these risks early, AEQUITAS enables proactive mitigation of biases, preventing them from being embedded in the system from the outset.
3. Development and evaluation
The development and evaluation phase is where fairness becomes measurable. Developers work with fairness metrics to assess how the AI system performs across different demographic groups, ensuring that the system is not biased against any group. Various mitigation techniques are applied, including pre-processing (e.g. data balancing), in-processing (e.g. adjusting algorithms) and post-processing (e.g. outcome fairness). This phase ensures that the AI system meets fairness criteria before it is deployed.
4. Deployment
Once the AI system is deployed, continuous monitoring ensures that fairness is maintained. The deployment phase includes transparency measures, such as model cards and datasheets, to ensure that the system’s operation is understood by all stakeholders.
5. Monitoring
Once deployed, the system must be continuously audited for fairness. Biases may appear over time as new data is introduced. Monitoring ensures that fairness issues are detected and addressed promptly, even after the system is in use.
6. Re-evaluation
The final phase involves re-evaluation of the system’s fairness metrics. As societal, legal and technological contexts evolve, AI systems must be continuously assessed to ensure they remain fair. Re-evaluation includes updating fairness metrics, adjusting algorithms and refining mitigation strategies to align with current legal requirements and societal values.
Controlled experimentation environment
AEQUITAS provides a controlled experimentation environment for testing AI systems against fairness criteria. This environment allows developers and researchers to stress-test AI models in controlled conditions, exposing them to different data distributions and testing their behaviour in fairness scenarios. The Synthetic Data Generator is crucial in this environment, enabling the creation of bias-free and polarised datasets to simulate real-world situations. If an AI system fails a fairness test, corrective actions are enforced, ensuring the system adapts and becomes more equitable before deployment.
This iterative testing and mitigation process is essential for developing AI systems that are both fair and compliant with legal standards. By using the controlled experimentation environment, AEQUITAS can ensure that fairness is not only a theoretical concept but also a practical, actionable measure in real-world AI systems.
Watch it in action here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=st6S8BH5gio&t=6s
The Experimentation Environment is available at https://aequitas.apice.unibo.it/en
Ensuring lasting impact
AEQUITAS is committed to ensuring that fairness in AI systems is not just a temporary focus, but a lasting and integral feature of AI development. To achieve this, AEQUITAS will be embedded into AI regulatory sandboxes, particularly through the EUSAiR initiative, allowing organisations to test AI systems in real regulatory conditions. This integration ensures that AEQUITAS remains a vital tool for developing AI systems that comply with evolving fairness standards. Additionally, AEQUITAS will be integrated into Italy’s IT4LIA AI Factory, which will provide continuous development opportunities and broader access, ensuring that the framework remains relevant and widely used for the long term. All consortium partner companies are committed to adopting AEQUITAS internally, utilising it to evaluate, certify or monitor AI systems within their respective domains. This real-world uptake will generate a sustainable user base, cement AEQUITAS as part of standard internal AI governance practice and create real use cases that further validate and improve the framework. This widespread adoption guarantees that fairness will continue to be at the forefront of AI development, even after the project concludes.
A final word from the AEQUITAS consortium
As we wrap up this journey, the AEQUITAS consortium would like to thank everyone who has been part of this project. Together, we’ve made important strides in shaping a future where AI is fair, transparent and accountable. Our collective work ensures that fairness will remain at the heart of AI development, and we are proud of what we’ve achieved. Thank you to all who contributed to making AEQUITAS a success.
Project summary
AEQUITAS (Assessment and Engineering of Equitable, Unbiased, Impartial and Trustworthy AI Systems) is an EU-funded Horizon Europe project advancing fair-by-design AI. This project aims to develop a controlled experimentation framework to diagnose and mitigate bias across the AI lifecycle, combining socio-legal and technical methods.
Project partners
AEQUITAS brings 16 partners from seven countries: UNIBO (coordinator), UMU, UCC, AOUBO; companies Philips, Adecco, Modis; SME LOBA; ICT competence centre ITI/UPV; and civil-society/think-tanks ALLAI, Eurocadres, Women in AI, PERIOD, Arcigay, Rayuela, plus ULL. This multidisciplinary mix combines AI research, data providers and rights organisations to co-design, validate, and scale fair-by-design tools and guidance.
Project lead profile
Roberta Calegari is an Assistant Professor at the University of Bologna (DISI; Alma AI). She coordinates the EU Horizon project AEQUITAS. Her research spans trustworthy/explainable AI, distributed intelligent systems, software engineering, multi-paradigm languages, and AI and law, with roots in symbolic AI and computational logic.
Project contacts
Roberta Calegari, Coordinator
Email: info@aequitas-project.eu
Web: www.aequitas-project.eu
LinkedIn: company/aequitaseu
YouTube: @aequitaseu
Instagram: @aequitaseu
X: @aequitasEU
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant agreement No. 101070363.
Views and opinions expressed are, however, those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Research Council Executive Agency.
Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Figure legends
Figure 1: AEQUITAS methodology.
Figure 2: AEQUITAS Consortium.