Advancing rare earth element-free solutions for Europe’s green transition
As Europe accelerates its shift towards renewable energy and sustainable mobility, the demand for permanent magnets (PMs) in applications such as wind turbines and electric vehicles (EVs) is surging. However, the reliance on rare earth elements (REEs) for PM production presents significant environmental, economic and geopolitical challenges. Addressing these concerns, the Horizon Europe-funded MagNEO project—Advanced Additively Manufactured Permanent Magnets for New Energy and Mobility Applications—aims to develop REE-free magnets using innovative additive manufacturing (AM) techniques.
Launched in May 2024, MagNEO seeks to revolutionise PM production by integrating advanced materials science with cutting-edge manufacturing processes. The project’s primary goal is to create robust, sustainable and high-performance magnets without the need for REEs, thereby reducing Europe’s dependency on imported materials and enhancing its technological sovereignty.
The critical need for sustainable magnets
Permanent magnets are integral components in numerous applications, including wind turbines, EV motors, industrial automation systems, robotics, aerospace components and various electronic devices. Traditionally, these magnets rely on REEs such as neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and samarium, which are predominantly mined and processed outside Europe. This dependency presents several critical challenges. Environmental impact is significant, as REE extraction and processing often result in soil and water contamination, greenhouse gas emissions and lasting ecological damage. Supply chain vulnerability is another concern, with the majority of REE production concentrated in a few non-EU countries, exposing Europe to geopolitical risks and market instability. Additionally, economic concerns arise from fluctuating REE prices, which can drive up manufacturing costs and create uncertainty for both producers and consumers.
The MagNEO project addresses these issues by developing alternative magnet materials that eliminate the need for REEs, focusing on sustainability, resilience and uncompromised performance.
The MagNEO vision
The MagNEO project is coordinated by SINTEF AS, a leading research organisation in Norway, and brings together 16 partners from ten European countries. The project is strategically designed to achieve five distinct objectives:
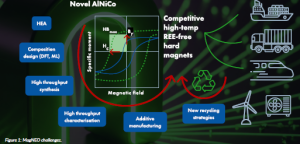
- Develop REE-free magnet materials, creating novel compositions of aluminium-nickel-cobalt (AlNiCo) alloys and high-entropy alloys (HEAs) suitable for additive manufacturing.
- Leverage advanced additive manufacturing techniques to produce complex magnet geometries with tailored microstructures, enhancing magnetic properties.
- Establish sustainable recycling strategies using environmentally friendly methods for recycling and reusing magnet materials, with a focus on cobalt recovery.
- Design for circularity by embedding end-of-life considerations in the early stages of magnet development to enable reuse and recyclability.
- Validate performance in industrial use cases by testing the developed magnets in realistic industrial scenarios across multiple sectors.
By integrating these elements, MagNEO aims to deliver magnets that meet or even exceed the performance of traditional REE-based magnets, while promoting environmental sustainability, economic viability and supply chain robustness.
What sets MagNEO apart?
Unlike conventional approaches that treat materials innovation, manufacturing and sustainability as separate silos, MagNEO takes a holistic and interdisciplinary approach. Key aspects include:
1. Innovative material compositions
MagNEO focuses on developing and optimising AlNiCo alloys and HEAs, known for their high-temperature stability, mechanical robustness and magnetic performance. These materials are specifically engineered to deliver enhanced coercivity, providing greater resistance to demagnetisation, an essential feature for high-performance, long-life applications. They also offer thermal and structural stability, ensuring that magnetic properties are maintained even in demanding environments, such as offshore wind farms and automotive powertrains.
Researchers are using computational modelling and experimental characterisation to fine-tune the magnetic, mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties of these alloys. The goal is to tailor the microstructure of materials for specific applications by controlling grain size, phase distribution and chemical homogeneity.
2. Additive manufacturing for magnet production
Utilising powder bed fusion-laser beam (PBF-LB) technology, MagNEO explores the advantages of AM:
- Complex geometries enable designs that are not feasible with traditional manufacturing methods, including shapes that improve magnetic field distribution and reduce material use.
- Microstructure control can tailor the internal structure of magnets to optimise their magnetic properties and minimise internal stresses.
- Resource efficiency minimises material waste during production by using precise, layer-by-layer fabrication.
- On-demand production facilitates local and flexible manufacturing, which enhances supply chain resilience.
Furthermore, MagNEO is exploring design-for-AM strategies that fully exploit the design freedom of AM, integrating functionality and reducing assembly complexity in the final components.
3. Sustainable recycling and lifecycle assessment
MagNEO focuses on developing innovative and scalable recycling processes to ensure the long-term sustainability of next-generation magnets. This includes direct recycling, which preserves the original microstructure and magnetic properties during the reprocessing of scrap materials, and indirect recycling, which involves recovering valuable elements, such as cobalt, from end-of-life magnets through hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical methods. Additionally, lifecycle and cost assessments are conducted to evaluate the environmental impact, economic viability, and social implications, ensuring the practical feasibility of the recycling approaches.
The project’s sustainability work package also explores policy implications, certification requirements and circular economy principles to support the broader adoption of sustainable magnets.
Applications and impact
MagNEO’s REE-free magnets are being designed for use in a range of high-impact sectors, such as:
- wind turbines, supporting low-speed permanent magnet generators, which are crucial for efficient renewable power generation
- marine propulsion, offering corrosion-resistant magnets for ship propulsion shafts, enhancing the sustainability of maritime transport
- automotive systems, including sensors, electric motors and safety systems such as ABS, contributing to the shift toward electric mobility
- industrial automation, powering actuators, sensors and motors in robotics and smart manufacturing environments
- aerospace components, enabling lighter, more efficient magnetic systems for aircraft and spacecraft
- consumer electronics, providing durable and sustainable magnets for devices like speakers, hard drives and wearables.
These applications demonstrate MagNEO’s broad industrial relevance, driving progress across sectors essential to Europe’s climate goals and digital transition. The project’s focus on high performance, recyclability and cost efficiency ensures that its outcomes can be implemented at scale.
From reducing environmental and geopolitical risks to enabling more sustainable design and engineering practices, MagNEO is poised to:
- accelerate the transition to clean energy and electric mobility
- increase European technological and industrial autonomy
- enable greener supply chains by reducing reliance on critical raw materials
- support climate-neutral manufacturing practices
- boost competitiveness in key strategic sectors, including automotive, aerospace and energy.
In the long term, MagNEO’s innovations could serve as the blueprint for other material-intensive industries seeking to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining performance and functionality. The magnet manufacturing ecosystem of tomorrow could be smarter, cleaner and more circular thanks to the pioneering efforts of this project.
Looking ahead
As the MagNEO project progresses, it aims to deliver several transformative outcomes by 2028:
- validating REE-free magnets that demonstrate consistent performance in demanding use cases such as renewable energy and electric vehicles
- developing scalable manufacturing processes that can be adopted across different scales of production, from prototypes to mass manufacturing
- establishing circular product design and recycling protocols: establishing processes that enable disassembly, recovery and reuse of critical materials
- supporting policy and standardisation by engaging with regulatory bodies to inform standards and certifications for REE-free magnet technologies.
The long-term vision is to position Europe as a global leader in sustainable magnet production, enabling the growth of clean technology without compromising the environment.
Through innovation, collaboration and a commitment to circularity, MagNEO is not only reshaping the future of magnet manufacturing but also reinforcing Europe’s leadership in the sustainable industry.
For more information on the MagNEO project, visit www.magneoproject.eu
Project summary
MagNEO is an EU-funded project that aims to develop sustainable REE-free permanent magnets using novel AlNiCo and high-entropy alloys via additive manufacturing, enhancing performance at high temperatures. By advancing eco-friendly recycling, particularly cobalt recovery, Europe’s reliance on rare earths is reduced, supporting the green transition in the energy and mobility sectors.
Project partners
The MagNEO consortium is an intersectoral team of 16 partners from ten different European countries. The consortium comprises a diverse range of professionals, including research organisations, technology providers, manufacturing companies, universities, standardisation specialists and experts in skill development, communication, dissemination and exploitation.
Project lead profile
SINTEF is one of Europe’s largest independent research institutes. With 2200 staff from 75 nations, it excels in technology, medicine and social sciences. As an independent non-profit organisation, SINTEF reinvests research profits into innovation and infrastructure, driven by its vision: “Technology for a better society.”
Project contacts
Dr Spyros Diplas, Project Coordinator, Research Manager, SINTEF
Email: Spyros.Diplas@sintef.no
Web: www.magneoproject.eu
LinkedIn: /magneo-project
Funding
Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are, however, those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Health and Digital Executive Agency (HADEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them. Grant agreement No. 101130095.
Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Disclaimer
Article coordinated and written by RTD-TALOS on behalf of MagNEO.
Figure legends
Figure 1: MagNEO challenges.
Figure 2: MagNEO Consortium.